Example 16
Determine the NAR implicit in a repayment schedule
This example demonstrates how to calculate the Nominal Annual Rate (NAR) of interest, akin to the Internal Rate of Return (IRR), that’s inherent in a standard repayment schedule.
As an engaging exercise, cycle through various day count conventions to compute the implicit interest rate, and witness firsthand how different time interval measurements in each convention can dramatically impact the outcome.
Understanding the Nominal Annual Rate (NAR) is crucial for anyone dealing with finance, as it reveals the true cost of borrowing or the effective return on lending. This example serves as a foundational guide for calculating NAR in a repayment profile, equipping users with the knowledge to assess the economics of any loan or investment, from the simplest to the most complex structures.
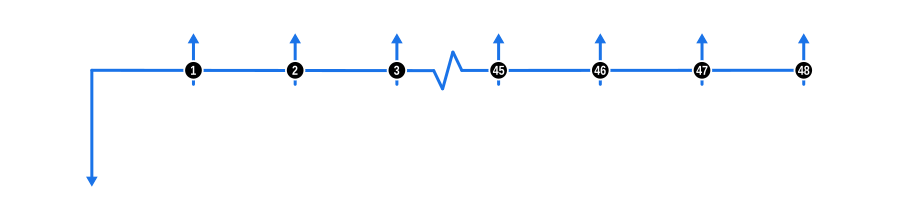
The diagram below visualises the cash flow dynamics of a standard repayment profile in Arrears:
Example Calculation Inputs
- Advance: Depicted by a blue downward arrow at the start of the timeline, this represents the full cash price or loan value, known from the outset.
- Payments: The blue upward arrows signify regular payments made in arrears, which means at the end of each payment period.
- Interest Rate: Since we’re solving for this, ensure the calculator’s interest rate field is empty.
TIP
Once you’ve mastered these calculations, why not grab your local newspaper or visit finance websites to find loan advertisements? Use the details from these ads to input into the calculator and verify if the advertised interest rate holds up under scrutiny.
Also try sketching your own cash flow diagrams to capture the financial cash flows. You’ll find over time it is a great way to break down seemingly complex problems into a single well understood diagram.
Benefits and Implications
- Transparency in Finance: Calculating NAR gives you a clear picture of the actual cost of borrowing or the yield on lending, promoting transparency in financial dealings.
- Comparative Analysis: Use this skill to compare different financial products. Even small differences in NAR can lead to significant savings or costs over time.
- Educational Value: This exercise is excellent for financial education, helping users understand how interest rates work across different conventions, which is vital when dealing with international finance where standards might differ.
- Negotiation Tool: Armed with this knowledge, you’re better positioned to negotiate loan terms or investment opportunities, ensuring you’re not overpaying or undervaluing your financial engagements.
- Spotting Discrepancies: By calculating NAR, you can quickly spot if an advertised rate doesn’t align with the repayment terms, which is crucial for consumer protection and informed decision-making.
This example not only sharpens your analytical skills but also empowers you to navigate the financial landscape with greater confidence and accuracy.